Introduction
When it comes to optimizing data storage, RAID configurations are often the first solutions considered. Among the most commonly discussed are RAID 1 and RAID 0, each offering unique benefits for different data management needs. RAID 1 vs. RAID 0 comparison highlights contrasting approaches in terms of speed, redundancy, and reliability. This article dives into these distinctions to help you select the right RAID setup for your specific requirements.
What Is RAID?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a storage technology that combines multiple disks to provide redundancy or improve performance. Different RAID levels achieve different goals by distributing data across multiple drives. Let’s look at RAID 1 and RAID 0 more closely.
RAID 1: Mirroring for Redundancy
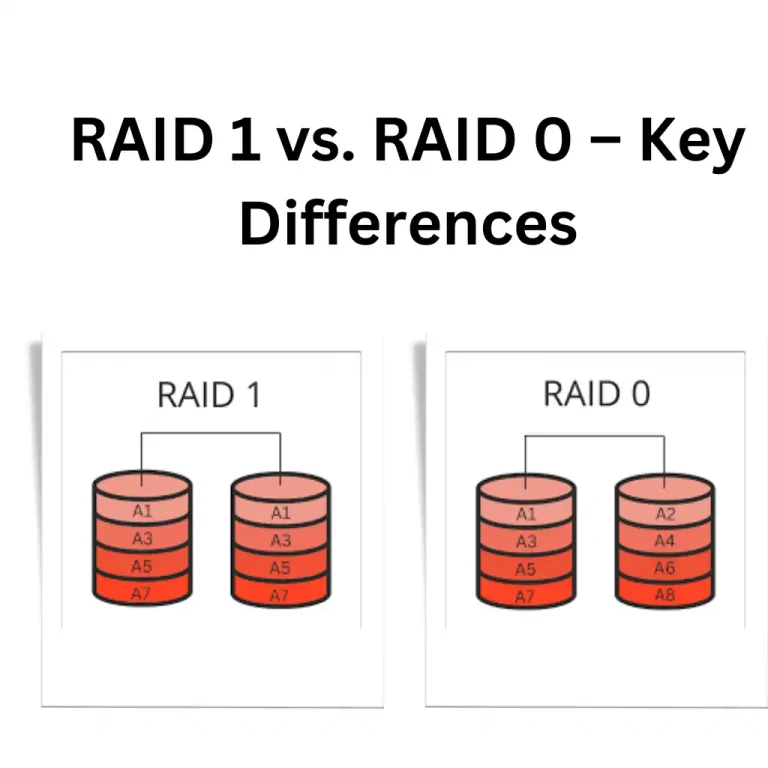
RAID 1, also known as mirroring, duplicates the same data onto two or more disks, ensuring that if one disk fails, the other disk still retains an exact copy of the data. This approach significantly boosts data security and redundancy, making RAID 1 ideal for critical data storage.
Benefits of RAID 1
- Data Redundancy: Provides 100% redundancy, ensuring data availability in case of disk failure.
- Reliability: The mirrored setup enhances data protection, ideal for sensitive or critical data storage.
- Easy Recovery: In the event of a disk failure, RAID 1 allows quick and straightforward recovery with minimal data loss.
Drawbacks of RAID 1
- Cost-Effectiveness: RAID 1 requires twice the storage, as each drive must mirror the other, which can be costly.
- Limited Performance Gains: While reliable, RAID 1 doesn’t provide the speed enhancements that RAID 0 offers.
RAID 0: Striping for Speed
RAID 0, known as striping, splits data across two or more disks, enhancing the speed and performance of data operations. Unlike RAID 1, RAID 0 does not offer redundancy, meaning if one drive fails, data on all disks in the array is compromised.
Benefits of RAID 0
- Enhanced Performance: RAID 0 provides faster read and write speeds, making it ideal for applications needing quick data access.
- Cost Efficiency: Since no redundancy is involved, RAID 0 makes full use of available storage, resulting in higher storage efficiency.
Drawbacks of RAID 0
- Lack of Data Redundancy: Data is not protected if a disk fails, making RAID 0 unsuitable for critical data.
- High Risk: With no backup, a single drive failure can result in total data loss.
RAID 1 vs. RAID 0: A Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | RAID 1 | RAID 0 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Redundancy | Yes, with mirroring | No redundancy |
| Performance | Moderate | High, ideal for speed |
| Storage Efficiency | Low (50%) | 100% (No mirroring overhead) |
| Cost | Higher (due to redundancy) | Lower |
Which Is Better for Your Needs?
For users who need reliable data backup, RAID 1 is an excellent choice. It suits applications where data integrity is critical, such as financial records or sensitive information. Meanwhile, RAID 0 is ideal for gaming, video editing, or any activity where speed is more important than data redundancy.
Conclusion
When choosing between RAID 1 vs. RAID 0, consider whether you value speed over safety or vice versa. RAID 1 ensures data security, whereas RAID 0 maximizes performance. Choose based on your data needs and risk tolerance.